Cognitive dissonance theory is a prominent social influence theory that was developed by Leon Festinger. It is used in behavioral modification such as in preventing alcohol abuse.
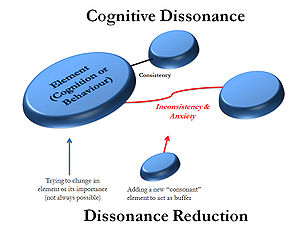
According to this theory, there is a drive towards cognitive consistency in humans. These cognitives are attitudes, behavior, and facts. When there is a inconsistency between two cognitions, the person experiences an internal discomfort. This makes the individual to remove that discrepancy and bring the cognitions into harmony.
For an example, we can ask a person who is abusing alcohol to join an anti alcohol public campaign. We can motivate him to do this by saying that it is not such a big deal and you can make new friends. In addition, if he is not willing to stop alcohol then we can say that he can continue drinking in other times and the participation is just a another event.
However, active participation in an anti alcohol campaign creates a cognitive dissonance in a person who abuse alcohol and it causes discomfort.
 | |
 | |
| Image via Wikipedia |
Most people will remove that discomfort by changing their attitude against alcohol. which will ultimately result in stopping the alcohol taking behavior. It is because changing the line of action that is already undertaken create more discomfort and it introduces the idea that the initial judgment to participate in the event is wrong. It is usually against one’s generally favorable view of oneself.
Actually anti alcohol campaigns are not much of a help to general public. However, they are effective in controlling alcohol intake in the people who actively participating in such programs.















No comments:
Post a Comment